Laparotomy: Understanding the Procedure, Indications, and Recovery.
Laparotomy is a surgical procedure that involves making an incision in the abdominal wall to gain access to the abdominal cavity. This technique allows surgeons to visually inspect and address various abdominal and pelvic issues. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of laparotomy, including its indications, the surgical process, and the recovery period.
To Know More About it Please Click Here
Understanding Laparotomy
Laparotomy is a major surgical procedure that provides a direct and extensive view of the abdominal organs. It is typically performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient remains unconscious and pain-free throughout the surgery. The incision made during a laparotomy can vary in size, depending on the specific purpose of the surgery and the region of the abdomen being addressed.
Indications for Laparotomy
- Abdominal Trauma: Laparotomy may be necessary in cases of severe abdominal injuries or trauma, such as those resulting from accidents or falls.
- Emergency Abdominal Conditions: Conditions like appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, or perforated organs may require immediate surgical intervention, often necessitating a laparotomy.
- Cancer Treatment: In some cases of abdominal cancers, a laparotomy is performed for tumor removal, organ resection, or biopsy.
- Gynecological Procedures: Laparotomy is commonly used in gynecological surgeries, including hysterectomy, ovarian cyst removal, or treatment of endometriosis.
- Organ Transplants: In certain organ transplant procedures, especially kidney transplants, laparotomy may be performed to access and prepare the abdominal cavity.
The Laparotomy Procedure
- Anesthesia: The patient is administered general anesthesia to ensure unconsciousness and pain relief throughout the surgery.
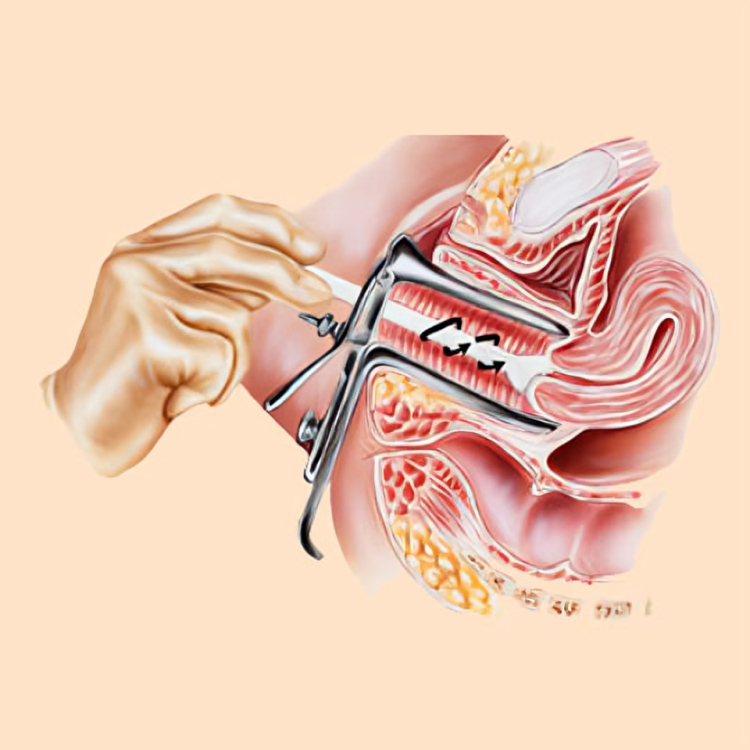
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in the abdominal wall, choosing the location and size based on the specific procedure and the area of concern.
- Exploration and Intervention: Once the abdominal cavity is accessed, the surgeon visually inspects the organs, addresses the issue at hand, and may perform necessary interventions, such as removing tumors, repairing damage, or resecting organs.
- Closure: After completing the necessary procedures, the surgeon closes the incision using sutures or staples, depending on the case.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
- Hospital Stay: The length of the hospital stay varies depending on the complexity of the surgery. Patients may spend a few days to a week in the hospital for observation and initial recovery.
- Pain Management: Patients are provided with pain medications to manage postoperative discomfort.
- Mobility: Gradual mobilization is encouraged to prevent complications such as blood clots and to promote healing. Early ambulation is crucial for a quicker recovery.
- Dietary Changes: Patients may start with a liquid diet before transitioning to solid foods based on their ability to tolerate and digest.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgical team are essential to monitor the healing process and address any concerns or complications.
To Know More About it Please Click Here
Conclusion
Laparotomy is a crucial surgical technique that plays a significant role in diagnosing and treating various abdominal and pelvic conditions. As with any major surgery, it is essential for patients to have a clear understanding of the procedure, its indications, and the expected recovery process. Open communication with the healthcare team and adherence to postoperative care guidelines are vital for a successful outcome and a smooth recovery.