PAP Smear: A Crucial Screening Tool for Women’s Health.
Regular screenings are essential for maintaining women’s health, and the Papanicolaou test, commonly known as the PAP smear, is a cornerstone in the early detection of cervical abnormalities and potential indicators of cervical cancer. In this article, we will delve into the significance of the PAP smear, its procedure, and the pivotal role it plays in preventive healthcare for women.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Understanding the PAP Smear
Named after its creator, Dr. George Papanicolaou, the PAP smear is a simple yet powerful screening test designed to detect abnormal changes in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus. These changes can be early indicators of cervical cancer or precancerous conditions, allowing for timely intervention and prevention.
The Procedure
- Preparation: Before the PAP smear, it is advisable to schedule the test when a woman is not menstruating. Additionally, patients are typically advised to abstain from sexual intercourse, the use of vaginal creams, and the insertion of tampons for at least 48 hours before the test.
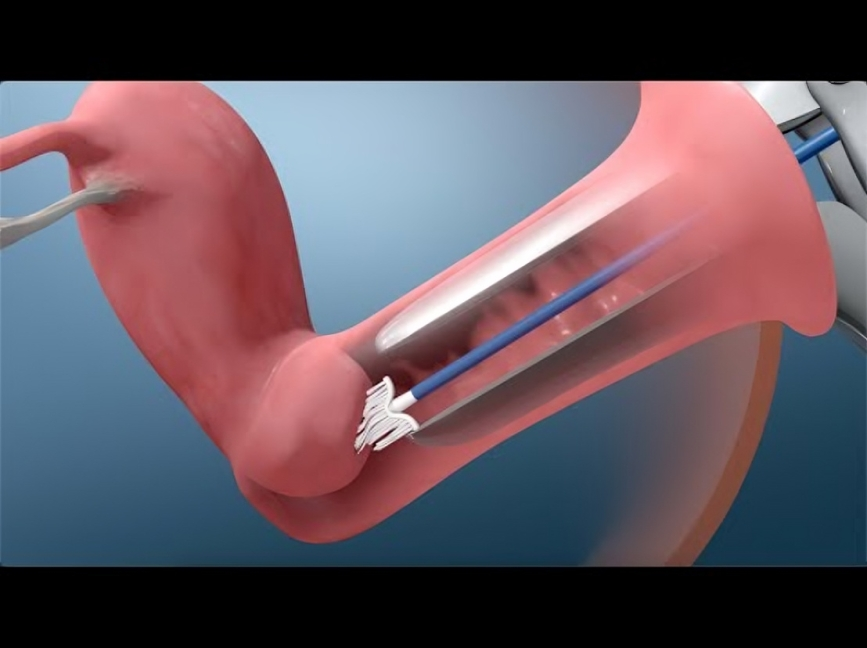
- During the Examination: The PAP smear is usually conducted during a pelvic examination. The healthcare provider will use a speculum to gently open the vagina, allowing access to the cervix. Using a small spatula or brush, the provider will collect a sample of cells from the cervix, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Frequency of Testing: The frequency of PAP smears depends on a woman’s age, medical history, and previous test results. In general, routine screenings are recommended every three years for women aged 21 to 65. Women over 30 may opt for co-testing, combining a PAP smear with an HPV (human papillomavirus) test, extending the screening interval to five years.
The Significance of PAP Smear
- Early Detection of Cervical Abnormalities: The primary goal of the PAP smear is the early detection of abnormal cervical cells, which could be indicative of precancerous conditions or the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV), a known risk factor for cervical cancer.
- Preventive Healthcare for Cervical Cancer: Cervical cancer is highly preventable and treatable when detected early. Regular PAP smears play a crucial role in preventing the progression of cervical abnormalities to invasive cancer.
- Guiding Further Diagnostic Procedures: If abnormal cells are detected, additional diagnostic procedures, such as colposcopy or biopsy, may be recommended to further evaluate the nature and extent of the abnormalities.
- Monitoring Treatment Efficacy: For individuals who have undergone treatment for cervical abnormalities or cervical cancer, PAP smears are essential for monitoring the effectiveness of the treatment and ensuring that any potential recurrence is detected early.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion
The PAP smear stands as a cornerstone in women’s preventive healthcare, offering a simple yet effective means of detecting cervical abnormalities and preventing the progression to cervical cancer. Regular screenings, coupled with appropriate follow-up and vaccination against HPV, contribute significantly to the overall well-being of women. It is crucial for women to engage in open discussions with their healthcare providers about the frequency of PAP smears, understanding that this routine test plays a pivotal role in safeguarding their reproductive health.